MATLAB: User defined functions
As you read this
material we strongly recommend that you activate your MATLAB window and try
the commands explained right there and then
MATLAB provides a convenient mechanism for using functions.
As we learned in C++, functions may receive data via their
arguments and return values to the calling program via their names and/or their
“passed by name” arguments. In C++, for
simplicity, we always wrote our user defined functions in the same file as our
main function. It is possible to write the C++ functions in their own files and
then link the files together properly.
In MATLAB , again for
simplicity, we will write each user defined function in a separate .m file and
consider them as scripts ( just like the rest of .m files), except that they
are going to be special scripts capable of receiving data and returning data.
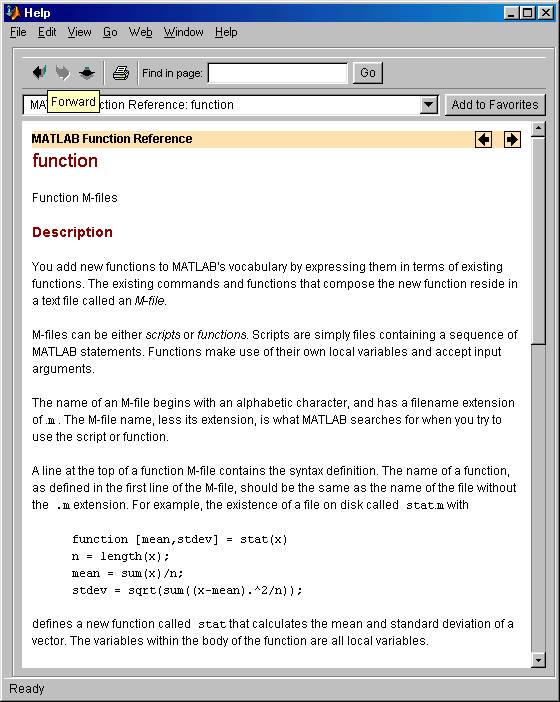
Here is what the HELP
facility of MATLAB has to say about function structure:
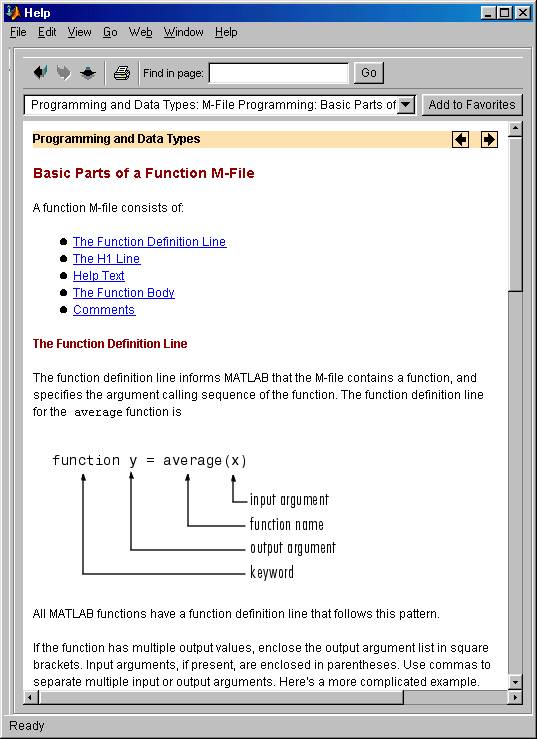

The name of the .m file must
be the same as the name of the function as indicated below by the Help
facility of MATLAB
We create a .m file which
contains the above function and save it on a folder on our desktop.
Here is the file named stat.m
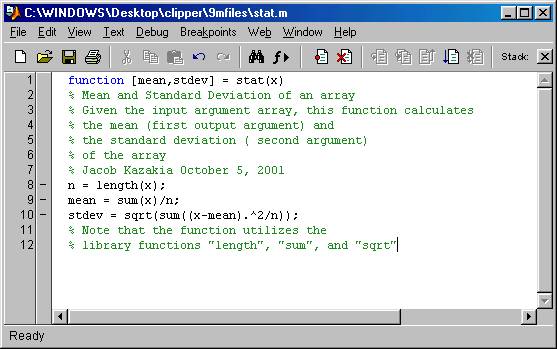
We can now use this function
by simply invoking its name. The use of
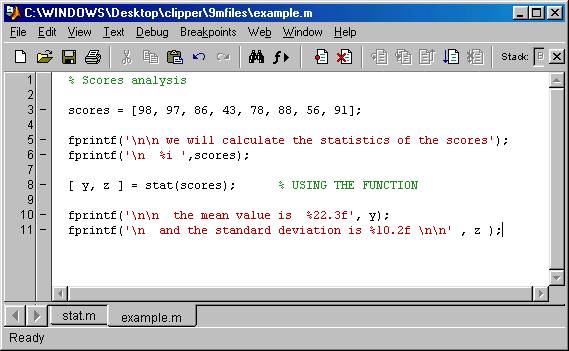
it is illustrated in the following picture of a script called , example.m where we
define an array of scores and then use the function to calculate the statistics
of the scores:
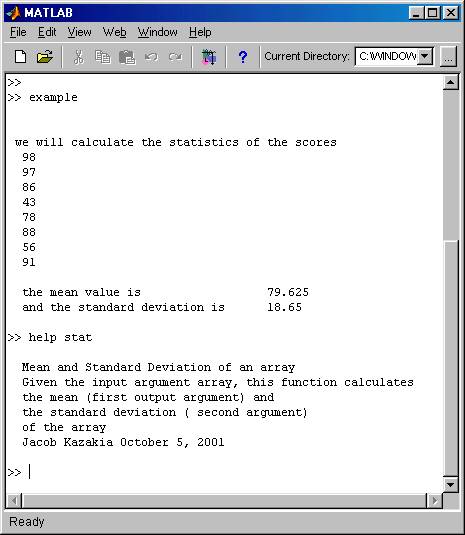
The following picture of the
command window illustrates the results obtained when we type the name of the
file example at the MATLAB command
line. It also illustrates that when we
type help stat we get the comments we
included in our function from the second line until the end of the uninterrupted
sequence of comment lines.